Floors on the soil
Replacing the wooden floors of the first floor in the old stone house on the floors on the ground. Click on the photo to enlarge.
Floor floors are a concrete floor of the first or base / basement floor, lying "right on Earth", i.e. There is no airspace between the floor and the soil. Floor floors are often made if the house is built on a ribbon foundation, i.e. The floor is poured between the walls of the tape. It is not recommended to build floors on the ground, if on the site is a high branch.
Such a floor should be:
- töples
- non-moisture
- relatively durable
Floor floors are a multi-layered design. Each layer performs a specific function. In this regard, the floors are similar to a slab foundation.
First, the extra fertile layer of soil is removed and the surface is spilled and tram. Then the pillow is made: the coarse sand is poured, rolls up and thoroughly tamper. From above, crushed stone from 10 cm and also thoroughly tamper. For the tamping sand / rubble cushion uses vibrating plates; It works on gasoline. If the workers do not have their own vibrating plates, it can be leased (it is inexpensive). Tamble and Radine rubble / sand is very important, it is impossible to save on this!
The useful feature of rubble is that it does not suck moisture from the soil. Smooth pillows need to check the laser level.
Many developers make a pillow in different ways: someone from sand, someone is only from rubble, someone from the layer of sand, and then layer of rubble. According to reviews, with the correct mischief, all these options work well. I remind you that crushed stone and coarse sand are good non-empty soils.
Top view of the pillow is made thin concrete black screed 3-5 cm. Its meaning is to create a smooth surface for laying waterproofing and insulation. Accordingly, it is not necessary to spend money on its reinforcement. After pouring the draft screed, waterproofing is stacked. It can be waterproofing films in two layers or bitumen waterproofing, it is necessary to watch money and angle.
Then the insulation is stacked - extruded polystyrene foam, which is much more durable than ordinary polystyrene foam and withstands significant loads. The insulation is needed that the floors are warm, about the same temperature as the air in the room. The EPPS also partially performs the function of waterproofing (except for its joints).
It is impossible to compare the insulation of the wall and floor on the ground. In winter, the soil under the residential house with the floors on the ground and the insulated gentle has a plus temperature, at least in the European part of Russia. Therefore, the EPPS is a thickness of 5 cm should be enough.
Next, on top of the insulation, a full-fledged concrete screed 5-10 cm (the thicker, the greater the load perceives). She will keep the finishing floor, partition; At the same time, it can be considered a heavy heat accumulator (this is a plus), because it is between the insulation and the room. Unlike the ordinary screed, for example, the slabs of overlappings, in the tie of floors on the ground, reinforcement (grid or reinforcement) must be necessary. It is usually reinforced by a welded grid 10x10 cm or 15x15 cm with a wire thickness of 3-6 mm.
On top of the main screed, the finish flooring is already mounted.
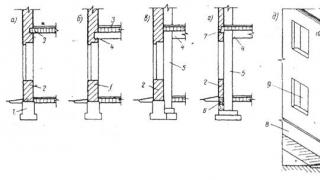
I described one of the popular gender structures on the soil, although in fact you can come up with several. Below the scheme:
 Here: 1 - the main screed (you can carry any finish coating on it), 2 - EPPS, 3 - waterproofing, 4 - rough screed, 5 - crushed stone / sand / crushed stone, 6 - natural soil, 7 - Ribbon foundation, 8 - Wall.
Here: 1 - the main screed (you can carry any finish coating on it), 2 - EPPS, 3 - waterproofing, 4 - rough screed, 5 - crushed stone / sand / crushed stone, 6 - natural soil, 7 - Ribbon foundation, 8 - Wall.
Please note that waterproofing enters the tape, i.e. Possible moisture from the soil completely complies with the room and walls. Also note that the insulation enters the tape, i.e., firstly, it partially complies with the cold, which comes from the tape, secondly, is a deformation seam. But still it is better to further insulate the ribbon outside and the break.
The deformation seam is needed if warm floors will be applied when the concrete screed can sharply heat up from the pipes in it and expand. If there are no warm floors, the deformation seam is optional.
People often change the festivities in order to save. Someone refuses waterproofing and all is well: the rammed crushed stone does not suck water up plus groundwater deeply. But this is still risk.
Someone refuses the insulation and warms the soil under the house. I would not have recommended to do so, with the insulation under the concrete screed, the cost of heating will be lower. I myself have a concrete floor on the soil without insulation and, if I had done everything, then Epps would definitely put it. It's not about heating expenditures, but to a greater extent in comfort, from the floor pulls cold. If there is a layer of EPPS under concrete, then the floor temperature will be almost the same as the air indoor.
Benefit from floors on the soil must be considered. Perhaps it turns out that it is cheaper to build ordinary "hanging" floors.
If the floors are selected, then it is necessary to warm the base of the foundation, otherwise it turns out the wool's bridge at the point of contact of the screed and tape base.
With the floors of the soil, of course, the arrangement is not required in the ribbon foundation of blood. But if the foundation is built and it is not yet clear that there will be overlaps or floors on the soil, then it is better to do it, and then, if it is decided to do half the floors on the ground, it can be found.