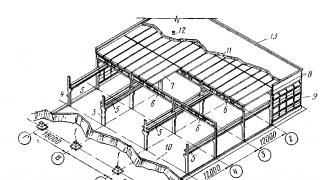
Despite the large variety of buildings for its intended purpose, volume-planning and constructive solutions, all of them consist of some limited number of interrelated parts or elements that are sometimes called architectural-structural elements.
According to the functional purpose, the elements of buildings are divided into:
- carriers that perceive the main loads arising in buildings and externally acting on them;
- enclosing, separating the building for individual premises protecting them from atmospheric influences and ensuring the required temperature in buildings;
- Elements that combine bearing and enclosing functions.
The main elements of the buildings (Fig. 1 and 2) are: foundations, walls, partitions, floors, roofs, coatings, separate supports, stairs, balconies, windows, doors, lights, crane beams, etc.
Foundations - underground bearing elements of buildings designed to perceive the load from the building and transferring it to the base.
The bases of buildings are soils under the bottom plane of the foundations, called the basement sole. If the load from the building is transmitted through the sole of the foundation on the ground, which is in the state of its natural occurrence, then such a soil is a natural base. Soils, pre-compacted or fortified by other methods, is customary to be called artificial foundations.
Fig. 1. Civil building elements
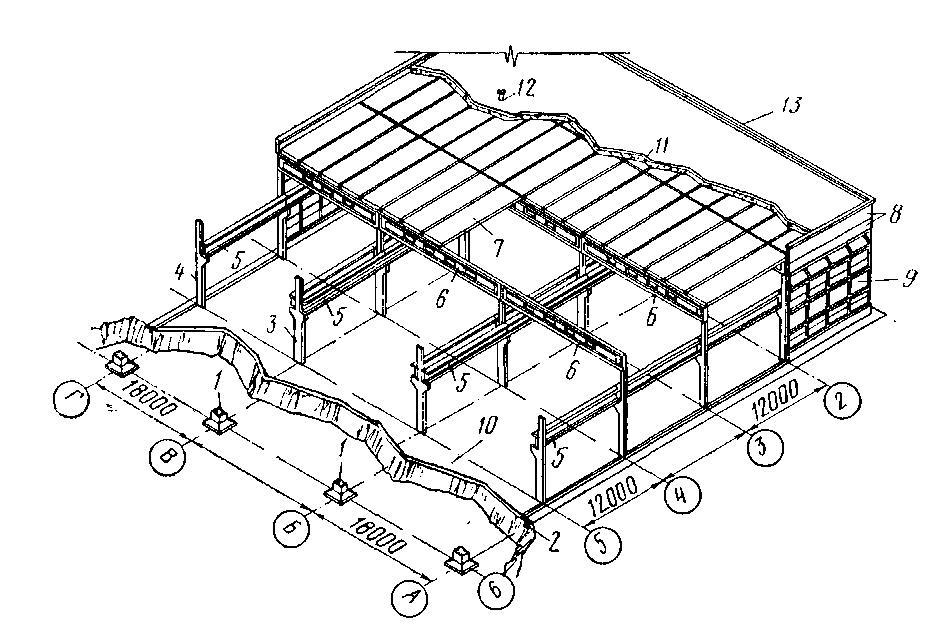
Fig. 2. Elements of one-story industrial building
Walls can be both enclosing and combining enclosing and bearing functions.
The walls on which, "roma of their own weight, are transferred to panels from other elements of buildings (floors, roofs, coatings, stairs), called carriers.
Walls that are only fences of buildings from external space and transmitting their own weight within each floor, relying on other supporting building structures, called nonsense. The same walls placed on the vertical designs of the building frame, is customary to be called mounted. If the walls are based on the foundations or foundation beams and on them, dick loads, droma of their own weight, do not act, they are called self-supporting.
The walls separating the premises in buildings from the external space and protect them from atmospheric influences are called outdoor, and separating some rooms within buildings from others - internal. The inner walls made of non-governmental materials in accordance with the requirements of fireproof standards as fireproof barriers are called firewall.
Partitions are enclosing elements and are intended to separate the internal space of buildings within each floor to separate rooms. In each floor, the partitions are based on overlap and their weight transmits.
Overlap are elements of buildings that combine enclosing and bearing functions. The floors are intended to separate buildings on the floors, limiting the room in each floor above and below. This is their enclosing function. In addition to their own weight and constant load on the weight of partitions, useful (temporary) loads on the weight of people, furniture, equipment and other items directly on the overlaps are affected. Perceiving and transmitting these loads to other supporting buildings of the building, overlapping performing support functions. At the same time. Performances, being horizontal diaphragms (discs), contribute to the increase in the spatial rigidity of the building as a whole, i.e. the immutability of its design scheme under the influence of various loads.
Overlapping, separating buildings on adjacent floors, is called internet; separating the lower floor from the soil - lower; separating the lower floor from the basement-overall; separating the upper floor from the attic - attic.
Roofs are also elements of buildings that combine enclosing and bearing functions. The upper waterproofing layer of the roof is called roof.
The enclosing functions of the roof consist in protecting the building from above from atmospheric precipitation, sun rays and wind. The carrier functions of the roof consist in perception and transmission to other supporting structures of the building of various loads (from people, snow, water, winds, various devices on the roofs, etc.), which can affect the roofs.
If there is a unheardered room between the roof and the attic overlap, the roof over such a building is called an attic. With gentle and flat roofs, as well as in industrial buildings, the attics are often not made, and the attic overlap is combined into one design with the roof, which in this case on civil buildings is called non-Cell or combined, and in industrial buildings - a coating.
Separate supports are carrier elements of buildings. They are performed in the form of columns, pillars or pylons and are intended to perceive loads from overlaps, roofs, coatings, bridge cranes, walls and transmission of these loads on buildings foundations.
Overlapping and coatings can be relying directly on columns and poles or through powerful beams based on them or farms.
Columns with such beams and farms make up the carrier frame of the building.
The stairs relate to the bearing elements of buildings and are intended for communication between the floors and in some cases with the attic and to go to the roof. In fire for fire purposes, the stairs in multi-storey buildings are arranged in separate rooms, stairwells having non-aggravated enclosing structures. In the staircases, in most cases there are also elevators that are also intended for communication between floors and for lifting goods and people to floors.
Elements of stairs - marches and playgrounds perceive the loads from people moving along them and moved goods and transmit these loads on the walls that protect the staircase, or on the bearing elements of the building frame.
Balconies are carrier elements of buildings intended to increase the performance of housing. In addition, balconies are one of the elements of architectural design of facades of buildings.
Erkers are also an expressive element of architectural design of facades. The Erker is a part of a residential room or other room, fenced from two or three sides, which has been rendered from the plane of the building, fenced from two or three sides. Erkers made in this way can be considered as a closed glazed balcony.
Loggias are balconies placed in the dimensions of the building, thus occupying part of the area and volume of the room, which could be heated. In addition to purely architectural significance, the loggias are rational use in a hot climate and on the southern facades of buildings in areas with temperate climates, preventing the premises from excessive overheating by sunlight.
In residential and cultural and domestic, mostly single-storey and low-rise buildings, often arrange an extension of a lightweight design - veranda.
The verandas are made glazed from all sides, partially glazed with a windward side or open, having only a roof, gender and railing around the perimeter.
The windows are enclosing elements of buildings intended for lighting and venting the premises. Doors are also enclosing elements of buildings intended for communication between adjacent rooms or between rooms and external space.
In industrial, agricultural and some civil buildings to explore in them and the export of large-sized equipment, products, materials and other goods, except doors, arrange the gate.
In the same buildings to illuminate the premises and their ventilation, if this cannot be carried out with the help of windows, light and aeration lights are arranged in coatings.
In a number of industrial buildings, bridge cranes and trails are used for performing intracerene transport operations, which are moving along the crane paths laid on special beams, called crane beams. Tanned beams - carrier elements based on consoles with special branches of the columns of the bearing frame of the building. Krap-beams are often moved along the lower shelves of steel 2-beam beams suspended to the bearing elements (beams, farms, etc.) of coatings or floors of buildings.
In addition to the elements listed above, there are visors over the entrances, entrance sites, the veils in the windows of basements, similarity in the basements, etc.
To ensure the necessary hygienic working conditions and life and the necessary comfort of living, working and in premises in the premises of people, buildings are equipped with sanitary, electrical, low-current and other devices and household equipment - heating, ventilation, water supply, hot water supply, sewage, gas supply, plates or furnaces for cooking, refrigerators, baths, souls, garbage supplies, electric lighting, electrical wiring for connecting household electrical appliances, radio, television antennas with wiring, telephonification, built-in furniture, kitchen equipment, sanitary assemblies, etc.