The roof is a structure that protects the building from above from precipitation, sunlight and wind. The upper waterproof shell of the roof is called the roof. The roof, together with the attic floor, forms the roof of the building. In the under-roof space can be located attic floor. In the event that there is no attic in the building, the functions of the attic floor and the roof are combined in one structure, which is called a non-attic cover.
Walls separate rooms from the outside (outer walls) or from other rooms (inner walls), thereby performing a protective function. In addition, the walls can bear the load not only from their own weight, but also from the overlying parts of the building (ceilings, roofs, etc.), performing a load-bearing function. Walls that perceive, in addition to their own weight, the load from other structures and transfer it to the foundations, are called load-bearing.
Walls resting on foundations and bearing the load from their own weight along the entire height, but not perceiving loads from other parts of the building, are called self-supporting. Finally, walls that serve only as barriers and carry their own weight within only one floor, relying on other important elements of the building, are called non-bearing.
Structural elements of buildings.The civic center of the city of Athens.Analysis of the ensemble of the Athenian Acropolis.
Despite the significant differences that exist between buildings for different purposes, both in appearance and in the internal structure, they all consist of a certain limited number of basic interconnected architectural and structural elements performing well-defined functions (Fig.)
The main elements of the building can be divided into the following groups:
a) bearing, perceiving the main loads arising in the building;
b) enclosing, separating the premises, as well as protecting them from atmospheric influences and ensuring the preservation of a certain temperature in the building;
c) elements that combine both bearing and enclosing functions.
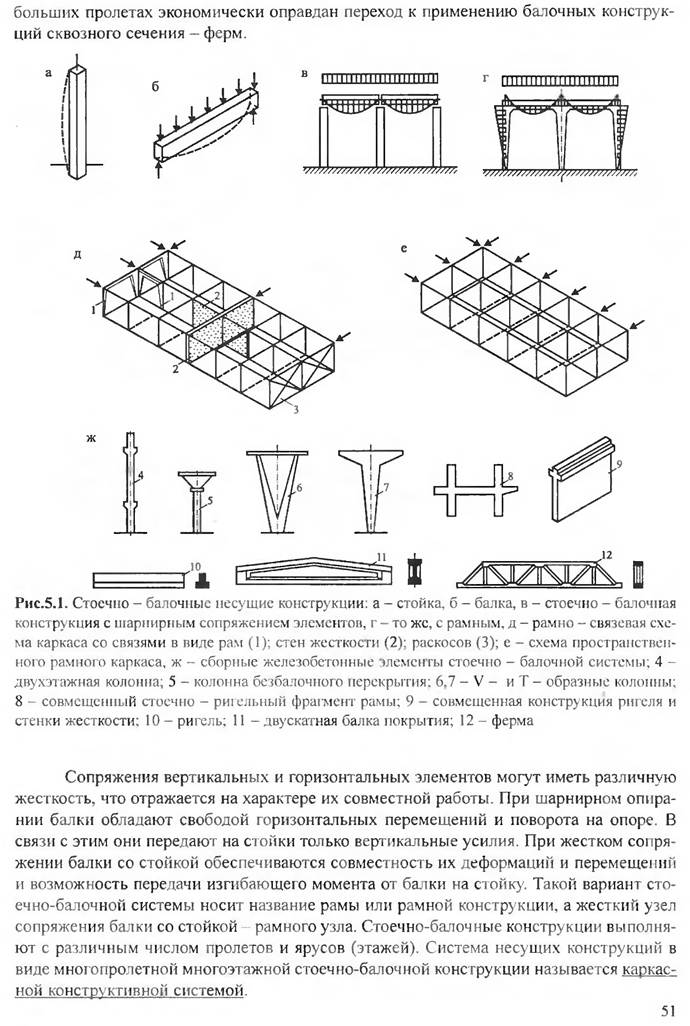
The load-bearing structures together form a spatial system - a combination of vertical and horizontal elements, which is called the load-bearing frame of the building.
Skeleton structures:
foundations,
floors,
free standing poles,
Bearing elements of the coating
foundation called an underground structure, the main purpose of which is the perception of the load from the building and its transfer to the base.
Overlappings called structures that divide the interior of a building into floors. Overlappings limit the floors and the rooms located in them from above and below (enclosing functions) and carry, in addition to their own weight, a payload, i.e. the weight of people, equipment and objects in the premises (bearing functions). In addition, floors play a very significant role in ensuring the spatial rigidity of the building, i.e. the immutability of its design scheme under the action of all possible loads.
Overlappings, depending on their location in the building, are interfloor separating floors adjacent in height; attic separating the upper floor from the attic; lower separating the lower floor from the ground, and above basement separating the first floor from the basement. On the top of the interfloor ceilings, floors are laid, depending on the purpose and mode of operation of the premises. And the lower surface of the floor (or cover) forms the ceiling for the underlying room.
Separate supports called racks (pillars or columns) designed to support ceilings, roofs, and sometimes walls and transfer the load from them directly to the foundations. Ceilings can be based either directly on columns, or, more often, on powerful beams laid along them, called girders. Columns and girders form the frame of the building.
Auxiliary elements:
1) partitions
2) filling openings (windows, doors, gates)
3) stairs
4) garbage chutes
5) engineering equipment (elevators, lifts, platforms, escalators, traversals, etc.)
6) other elements (balconies, loggias, sanitary cabins, etc.)
7) elements that provide spatial rigidity of the building
8) building ventilation elements
Partitions relatively thin walls are called, which serve to divide the internal space within one floor into separate rooms. The partitions are supported in each floor on the floors and do not carry any load other than their own weight.
stairs serve to communicate between floors. For fire protection reasons, stairs, as a rule, are enclosed in special, walled rooms, which are called stairwells.
To illuminate the premises with natural light and for their ventilation (ventilation) are used window, and for communication between adjacent rooms or between a room and an outdoor space - doors. In some cases, if it is necessary to introduce large equipment or means of transport into the premises, in addition to doors, gates are also arranged.
These and many other structures and elements will be discussed in the lecture course.
According to the nature of statistical work, all load-bearing structures are divided into planar and spatial. In planar - all elements work autonomously under load, as a rule, in one direction, and do not participate in the operation of the structures to which they adjoin. In spatial - all or most elements work in two directions and participate in the work of structures mated with them.
This increases the rigidity and load-bearing capacity of spatial structures and reduces the consumption of materials for their manufacture.
The choice of the type and material of load-bearing structures during design is determined by the spans to be covered. For small spans, simple planar and rod structures are used, for large spans, more complex spatial ones.
There are several types of main bearing elements - rods, plates (plates), spatial shells and massive or three-dimensional bodies.
Kernel(stand) - the simplest element, in which two dimensions (thickness and width) are small compared to the third - length.
plate(plate) is an element in which one dimension - thickness - is small compared to the other two. Curved slabs are called shells.
massive are elements in which all three general sizes are approximately the same order.
Rice 
The main types of load-bearing elements:
a - rod; b - plate; c - shell; g - massive body